Whaling Attacks in Cybersecurity: What is it & How it Works

Level-C employees, CEOs, and CFOs beware of whaling phishing attacks. They are here to steal sensitive information from your company.
If you are a chief executive officer, a chief financial officer, or working at a high profile in a company, beware, cyber attackers are coming for you. Does this line make you wonder how your position in a company can make you a target? Well, that is the catch.
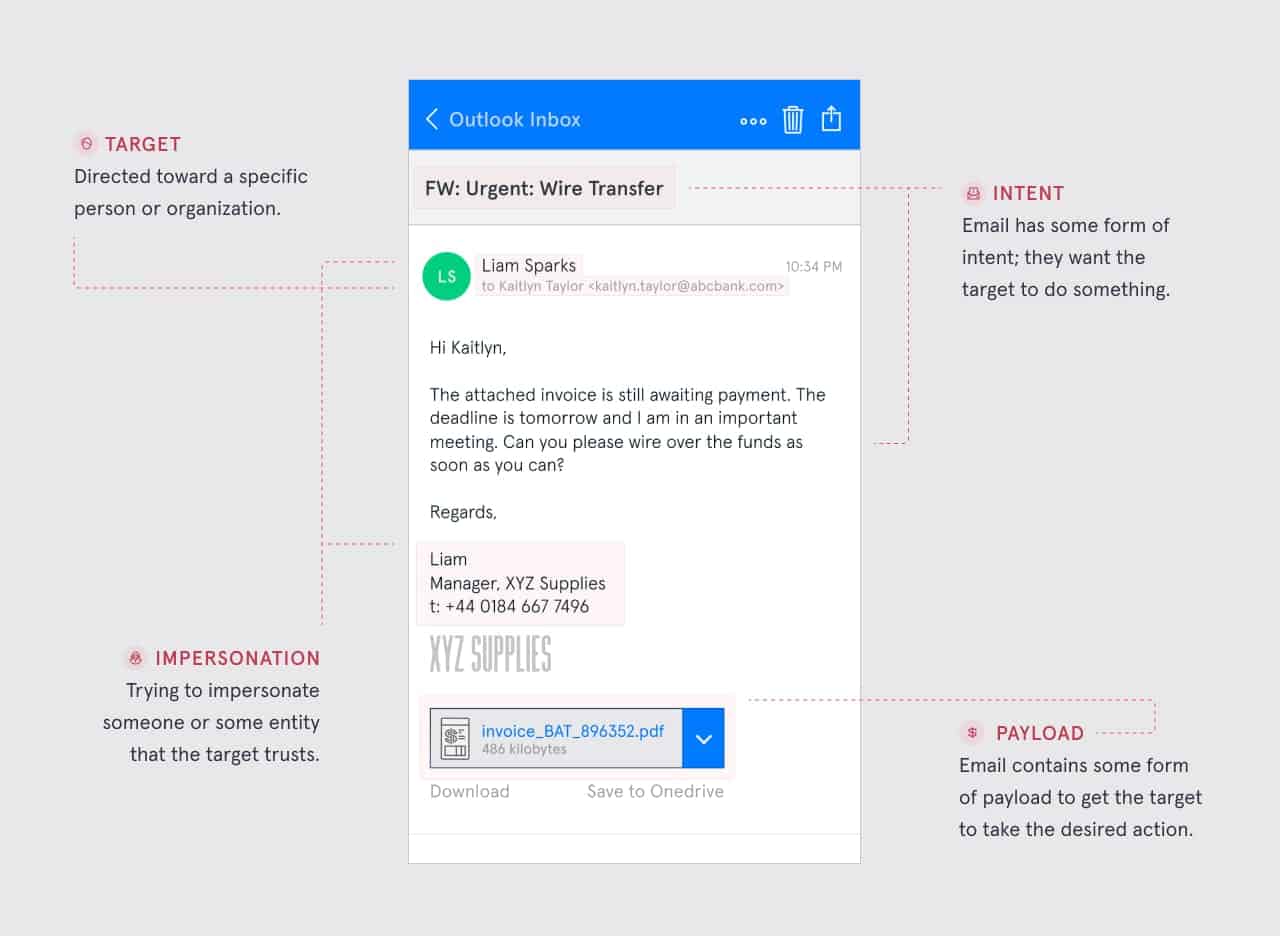
A whaling attack is a type of phishing attack that targets individuals with authority in a company. Whaling cyber attacks aim to manipulate a victim into authorizing high-value wire transfers to the attacker, making them ominous. This makes understanding whaling attacks, how they work, and how to stay protected from them essential.
Fact Check – According to Verizon, around 25% of all data breaches result from phishing.
What Is Whaling Attack?
Whaling is the term used when fishermen go into the sea to hunt whales for food and oil.
The same is true in cybersecurity. Here, attackers like the fisherman send phishing emails to target high-level professionals (whales, the largest fish in the sea) for money, and information, spreading malware and weakening the company’s supply chain.

Get Started w/ NordVPN Today
- Top-rated VPN for OS unknown
- Ultra-fast speed in US in 2024
- Save 69% off with VPN.com Discount
- Plans starting at $2.99/month
GUARANTEE
What is whaling in cybersecurity & how do whaling attacks work?

It is a type of social engineering assault that targets valuable information. When this information is obtained, it can provide the attacker with a means to access a company’s intellectual property, customer data, or other potentially profitable data that they can sell on the dark web.
To perform a whaling attack targeting high-level executives, cybercriminals first collect personal information about the target organization or individual using social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
Once they have all the information, attackers send highly personalized emails, incorporating specific details like the target’s name and job title with business language and tone, making it difficult to distinguish between scam and real email.
This creates a sense of urgency and tricks victims into divulging sensitive information, making a write transfer, or clicking on links that infect their system with malware. Besides this, there are other objectives for creating a whaling attack.
Objectives of Whaling Phishing Attacks
Control: To breach the company’s network and move to connected networks within the organization to potentially gain administrator access.
Money: To transfer money to themselves by unlawfully accessing target accounts.
Corporate Intelligence: To obtain business secrets or other intellectual property related to the organization and sell it to competitors or other countries.
Supply Chain: To gain knowledge about the organization’s weak points within the supply chain and use them for their benefit.
Personal Smear Campaign: To perform other types of attacks and send across smear campaigns to tarnish an organization’s or individual’s image.
Malware Circulation: To spread and install malware such as rootkits, ransomware, and keyloggers on the victim’s computer systems.
Types of whaling attacks
There are several types of whaling attacks, and they include:
- Making a phone call to the employee impersonating the CEO or CFO to corroborate the email request.
- Sending emails with credible information about the suppliers or partners to make them look genuine.
- Threat actors even send such emails that appear to be from colleagues or senior executives.
Examples of whaling attacks

Over the years, there have been many whaling attacks. Here are some examples:
2016: An Austrian aerospace manufacturer named FACC employee, was sent a whaling email to transfer money to an account for a fake acquisition project – a kind of scam known as a “fake president incident.” This made the CEO lose his job, and the company suffered a loss of $58 million.
2016 Whaling Attack targeting Snapchat’s payroll department where attackers sent phishing emails posing as the CEO to obtain sensitive employee payroll information.
2016 the Seagate attack – Through a whaling attack, the attacker made an employee unwittingly share the W-2 (income tax forms) and the personally identifiable information (PII) of the company’s current and past employees. This breach exposed thousands of people’s personal information.
2016 toy giant Mattel fell victim to a whaling attack after a top finance executive received an email requesting a money transfer from a fraudster impersonating the new CEO. The company almost lost $3 million as a result.
2017: Through a man-in-the-middle whaling attack, hackers made a move and cost a small business owner $50,000.
2018 Pathé, a European cinema company, suffered a whaling attack resulting in a loss of $21.5 million. The attackers, impersonating high-ranking executives, tricked the CEO and CFO into transferring approximately $800,000, leading to significant losses.
2020: Cybercriminals using a malicious link, attacked the co-founder of an Australian hedge fund, making them mistakenly approve $8.7 million in fraudulent invoices and forcing the business to close.
Who are the targets?
Whaling attacks can be performed without high technical knowledge, bringing substantial profits and making them a major threat to businesses.
However, financial institutions and payment services are the most targeted organizations. Recently, cloud storage and file hosting sites, online services, and e-commerce sites have been targeted and becoming vulnerable to whaling cyber attacks.

Get Started w/ NordVPN Today
- Top-rated VPN for OS unknown
- Ultra-fast speed in US in 2024
- Save 69% off with VPN.com Discount
- Plans starting at $2.99/month
GUARANTEE
Consequences of Whaling Attacks

Financial Loss:
Whaling attempts generally make the employee do a wire transfer falling for the scam and sending significant amounts of money. This causes businesses to lose their money, pay fines for data breaches, and face the potential loss of customers.
Data loss:
Besides financial loss, a whaling attack also results in data breaches. This can result in significant fines under GDPR.
Disruption:
Dealing with the aftereffects of an attack can be challenging. When companies focus on securing things, they spend most time notifying customers and relevant parties of the data breach. This not only makes them lose business but also there is an upheaval in the working of the working.
Brand damage:
When an employee becomes a victim of impersonation fraud and a data breach, it harms the company’s reputation and credibility with customers and partners. This leads to missed opportunities and harm to the company’s brand image.
How to recognize a whaling attack

Identifying a whaling attack can be challenging as attackers invest considerable time and effort into making their emails and websites look authentic. However, there are some common signs that, if kept in mind while replying to a mail, can save you or your company from being a victim of a whaling attack.
This includes the sender’s email address, a request to share sensitive information or transfer money, and a sense of urgency or threat of consequences. To help remember the steps, let us use the acronym WHALE:
- W – Who that Sender is: Check the sender’s mail address for misspellings or discrepancies in the sender’s email address (domain).
- H – How is the Subject Line Written: Be extra cautious with subject lines. If you see one with an extra sense of fear, urgency, or panic, try connecting with the concerned person over a personal number.
- A – Attachment Inspection: Watch out for file types, as threat actors use them to hide malware. Before downloading an attachment, check using an antivirus like T9. Moreover, you can use a Systweak VPN to hide your IP address and prevent others from tracking you online.
- L – Look at the Content: Don’t trust the information because it appears authentic. Verify it yourself and look for telltale signs.
- E – Elect to Confirm the Request: Always double-check suspicious requests by contacting the sender. The best way is to connect personally. However, if that is not possible, get the personal numbers unavailable online and connect with the concerned person.
How to block a whaling attack?

Blocking whaling attacks is not something that you can’t do. The organization can prevent whaling attacks by putting certain security measures in place. This includes:
- Implementing a multi-layered security approach using anti-spam and anti-malware software that will help intercept suspicious emails.
- Employing DNS authentication services like DMARC, DKIM, and SPF protocols to verify the legitimacy of emails from a specific domain.
- Real-time email scanning and filtering technology to detect and block suspicious attachments and links.
- Using anti-impersonation software to identify social-engineering tactics used in whaling emails.
- Provide awareness and security training to employees to help them recognize and respond to whaling attacks.
Ways to protect against whaling phishing

To protect against whaling attacks, a comprehensive approach is necessary, which includes employee awareness, data detection policies, and enhancing infrastructure. Below are some best practices for preventing yourself or the company from being a victim of a whaling attack:
- Every employee, not just executives, should be trained to identify whaling attacks and what social engineering tactics to look for.
- Multistep verification should also be in place for requests for wire transfers and access to sensitive data.
- Organizations should establish data security policies that monitor emails and files for suspicious network activity, providing a layered defense against whale phishing and phishing in general.
- High-level executives should know social media’s potential role in enabling a whaling breach. Companies should educate them so that they can avoid sharing personal information over social media platforms that cybercriminals can exploit.
- Use anti-phishing software and security services to help prevent whaling and other phishing attacks. The T9 antivirus is a great tool for securing PCs from real-time threats.
- Educate everyone and yourself on identifying phishing emails that differ slightly from the trusted address, requests for money or information in the email body, and a domain age that does not match the trusted correspondents.
- Exercise caution when accessing links or attachments received in an email.
- Foster a “trust but verify” culture within the organization, urging employees to confirm the legitimacy of urgent messages through alternate channels such as face-to-face interactions or phone calls with the sender.
- Establish a phishing awareness training program that targets whaling attacks. The program should be tailored for senior management and employees who interact with the public and include simulated whaling attacks to help workers recognize potential phishing schemes. The focus should be on learning from mistakes within a secure training tool.

Get Started w/ NordVPN Today
- Top-rated VPN for OS unknown
- Ultra-fast speed in US in 2024
- Save 69% off with VPN.com Discount
- Plans starting at $2.99/month
GUARANTEE
How is whaling different from phishing and spear phishing?

Generally, people get confused between phishing, whaling, and spear phishing attacks and use them interchangeably. Though all three are online attacks designed to obtain sensitive information or manipulate the victim into taking harmful action, they aren’t the same.
Whaling phishing attacks are a specific form of spear phishing targeting high-ranking individuals within a company. On the other hand, spear phishing attacks can target any individual. In contrast, phishing is a broader term encompassing any attack that tricks a victim into sharing sensitive information, installing malware, or performing a fraudulent financial transaction.
While regular phishing emails typically get sent to a large number of individuals without knowing how many will fall for it, whaling emails are highly personalized and directed towards one specific individual, usually a high-ranking person, with tailored information.
Whereas phishing scams target non-specific individuals and spear-phishing targets particular individuals, whaling doubles down on the latter. It targets not only key individuals but also the entire organization as the fraudulent communications they send make businesses lose millions and individuals lose their jobs. So do not take it lightly, don’t mistake it as a typical phishing scam you can recognize. It is very deceptive, and its urgency leaves no room for the person the mail addresses to think and act.
Watch Out for Whaling Campaigns. They Might Be In Your Inbox!
In conclusion, whaling attacks are getting more sophisticated each day, and with work-from-home becoming prevalent, companies are now more prone to them than ever. Therefore, be cautious when acting upon a request received by email. There are several consequences of whaling attack phishing scams, so stay vigilant and watch out for any phishing indicators.
Whaling attacks can target anyone, even those with high technological expertise and corporate entities. Hence, it’s essential to comprehend how cyber scams operate and to identify the signs of a phishing campaign to safeguard your personal and business reputation.
Stay Safe and Be Cautious.
Sakshi Sharma
Guest Author
Sakshi Sharma is a member of Tweaking Technologies. With her expertise in content blogging and a deep understanding of technological trends, she plays a pivotal role in content outreach, ensuring that their offerings are effectively communicated and resonate with their professional audience.
Customer Reviews for NordVPN: In-Depth Review, Tests, and Stats
Connection issues with MLB.TV
May, 2 2023

Prompt customer service
May, 6 2023

I would highly recommend
December, 15 2023



